LEDs are solid-state light-emitting devices. Compared to traditional light bulbs, they generate less heat and have a longer lifespan. Additionally, they can form compact, all-solid-state light sources with excellent impact resistance, significantly enhancing design flexibility for customers. This article explains the basic structure of LED components.
What is an LED?
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a light-emitting component made from semiconductor materials. When packaged for use as an electronic component, it is collectively referred to as an LED. In this article, the packaged product is called an "LED" (or "LED component"), while the semiconductor element itself is referred to as an "LED chip" for clarity.
LEDs are widely used in applications that leverage their small size and low power consumption, such as indicator lights for electronic devices, information display panels, and LED screens. With advancements in high-power output, they are now also used in lighting applications, including LCD backlights, camera flashes, and, thanks to advancements in white LEDs, general indoor/outdoor lighting and automotive headlights.
Types and Structures of LED Components
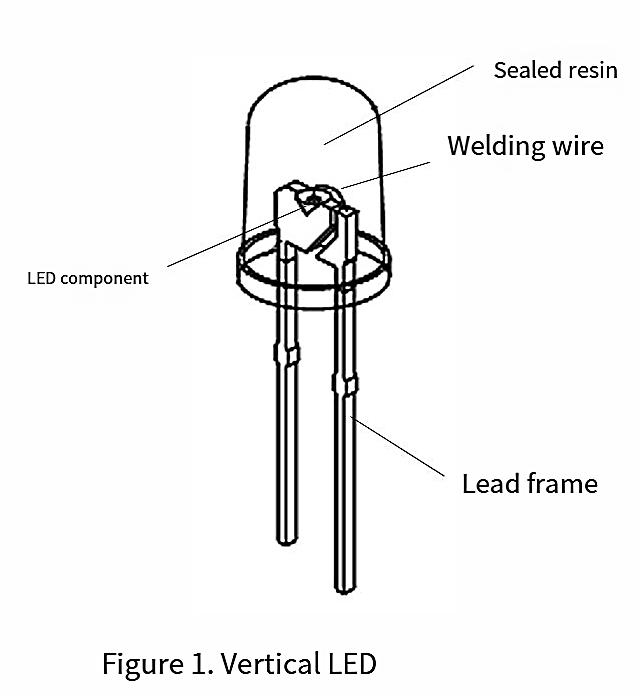
Longitudinal LED
The main structure includes the LED chip, lead frame, bonding wire (gold wire), and encapsulating resin. (Figure 1)
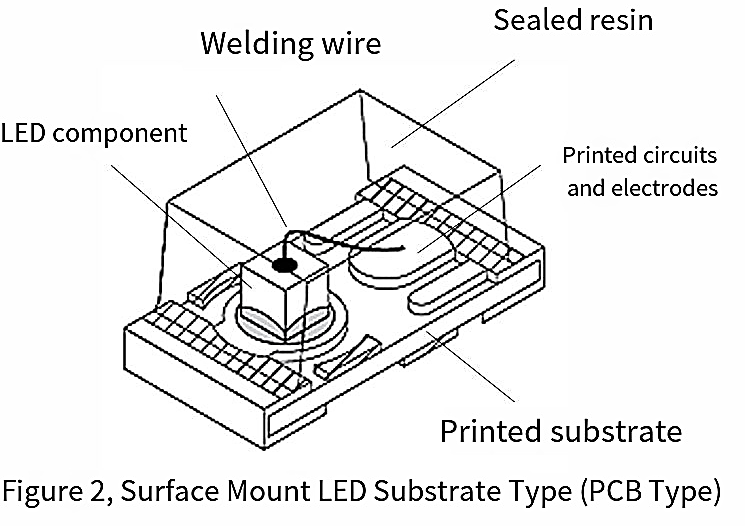
[Surface-Mount LED (PCB Type)]
Designed for surface mounting on circuit boards (Figure 2). The structure involves placing the LED chip on a small printed circuit board (PCB) with pre-printed circuitry, connecting it via bonding wires, and securing the assembly with encapsulating resin.
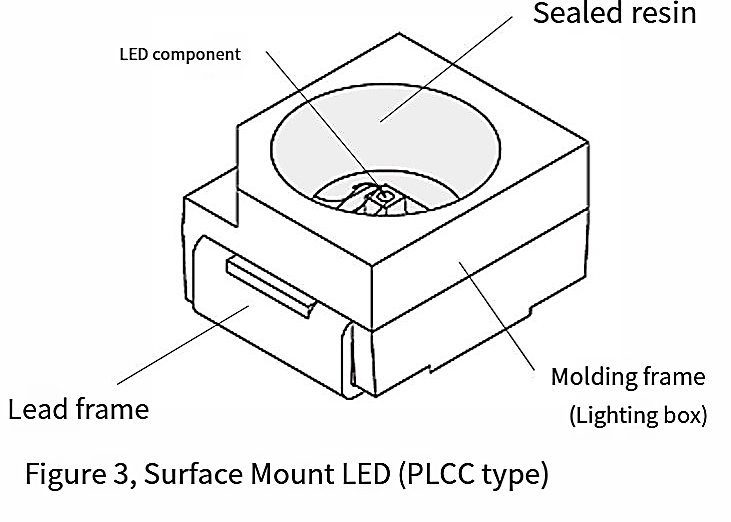
[Surface-Mount LED (PLCC Type)]
Unlike the PCB type, this design integrates a lead frame and a molded reflector (housing) into a single package. The LED chip is mounted inside, connected via bonding wires, and encapsulated with resin. The reflector enhances light distribution and efficiency. (Figure 3)
[Other Surface-Mount LEDs]
Variants include ceramic reflectors or glass covers instead of resin encapsulation.
Components of LED Devices
LED Chip
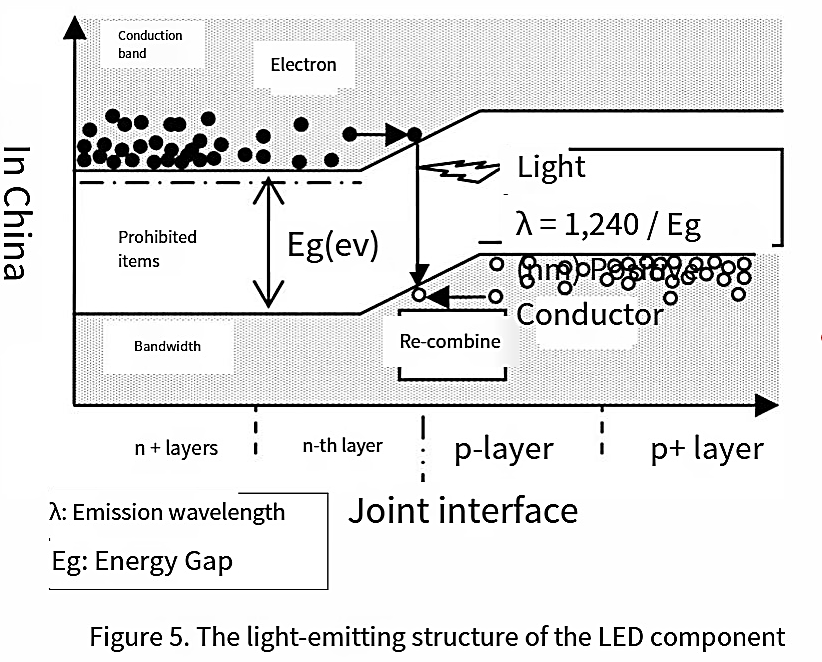
The core component of an LED. It is a semiconductor-based photoelectric conversion device that transforms electrical energy into light. Its basic structure consists of a p-n junction formed by different semiconductor materials (e.g., GaAs, GaP, AlGaInP, InGaN). (Figure 4)
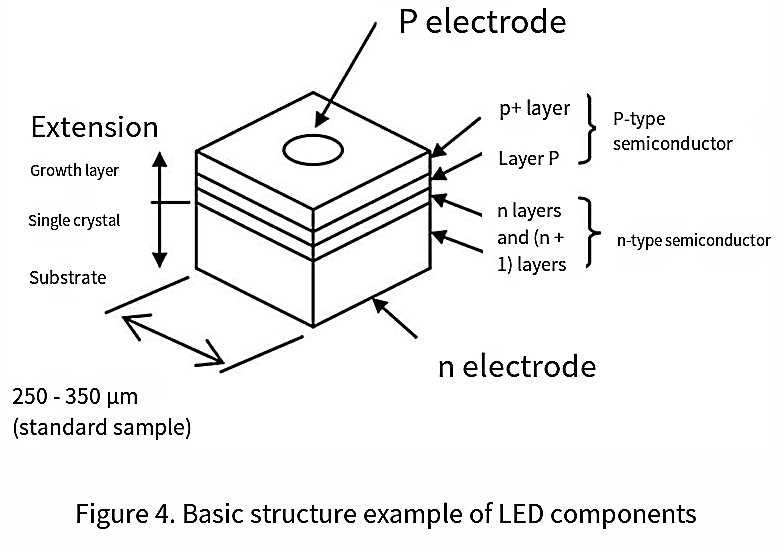
Common diodes mainly use materials such as silicon and germanium, while leds employ compound semiconductors like GaAs, GaP, AlGaInP, and InGaN. The electronic energy state within the solid state of compound semiconductors varies depending on the constituent materials. It has the property of converting electronic energy into light energy within it, and the wavelength of light is inversely proportional to the energy of electrons. LED uses compound semiconductors. Depending on the constituent materials, it can obtain light of different wavelengths such as infrared, visible light, and deep ultraviolet.
The electronic energy is converted into light energy to electricity, the element to the pn junction of injected carrier. In N-type semiconductors, the carriers are electrons. In P-type semiconductors, the positive holes (a special collection of electrons that move in a state similar to a positively charged particle under the action of quantum mechanics) are equivalent to carriers. When electrons and positive holes meet at the pn junction, they recombine and the charge disappears. At this point, the energy possessed by the electrons is released. Energy is released in the form of electromagnetic waves, thereby extracting light.
To enhance the actual luminous efficiency of LED components, we have carried out a lot of designs. The luminous efficiency of components can be divided into the efficiency when converting electron energy into light energy (internal quantum efficiency) and the efficiency when releasing light energy from the component to the outside. The efficiency of the photoelectric conversion phenomenon is usually expressed by treating both electrons and light as quantifiable quanta one by one.
External quantum efficiency: 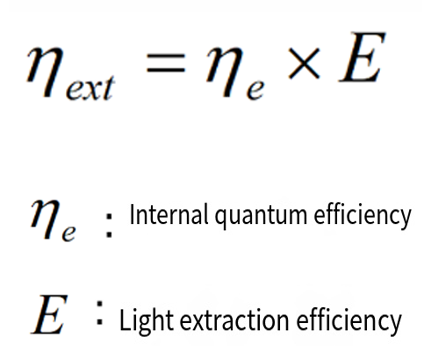
To improve the design of the internal quantum efficiency
² It mainly involves the design of the pn junction part
² Increased crystallinity, heterojunction, quantum well structure, etc
Add a design for light extraction
² Eliminate the light-absorbing elements within the LED components and reduce the internal reflective components.
² Design of the component substrate part – Transparent substrate is adopted
² Reduce internal reflective components – surface texture treatment, trapezoidal shape, etc. – to form reflective layers, etc
To sum up, the LED component itself is all-solid-state, which can achieve all-solid-state light-emitting components with tough mechanical performance. In addition, since the luminescence is not caused by heat, it is expected to achieve high luminous efficiency.
Lead Frame / PCB
Maintain the LED components, accept external power supply, and conduct electricity on the components. Copper or iron alloy lead frames are used in longitudinal LED and PLCC packages. Since it is necessary to receive the light from the LED components at close range, a design that uses a high-reflectivity coating to suppress the light absorption within the LED is usually adopted. Printed circuit boards (PCBS) are often used in LED chips. To suppress light absorption, the printed substrate will also use materials with high reflectivity.
The important role of lead frames and PCBS is to dissipate heat from components. This is an important path for direct contact with components to release the heat generated by the components. In applications that require high-power optical output, large currents need to flow through. Various designs have been adopted in the packaging, such as using more diverse lead frames and metal cores in the PCB.
Bonding Wire
The conductive parts of the lead frame and PCB as well as the electrodes of the components are mainly soldered with gold wire. Welding uses ultrasonic waves. At the beginning of the welding process, the top of the gold wire is spherical, and it is welded by friction with the component electrode or lead frame using ultrasonic waves. The ball can be made by discharging and heating to melt the top part of the gold wire. (figure 6)
When the ball near the line will be partial melting, cooling after the show different from other parts of state (known as recrystallization region). This part will form grain boundaries and requires attention from an electrical perspective. For instance, the wire may break when a large current flows through it. When designing the rated value of an LED, the margin should be fully considered to prevent disconnection.
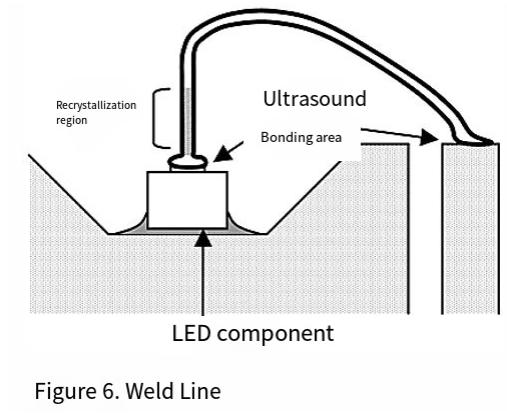
In terms of mechanical strength, the solder wire is one of the vulnerable parts of the LED, but it has been protected by fixing the area around the solder wire with sealing resin and the like.
Die-Attach Material
It is used to fix LED components on lead frames, etc. Most LED components have current flowing from the epitaxial growth layer to the conductive substrate side. Therefore, the following structure is adopted: the component is installed on the current path of the lead frame or PCB, bonded to the substrate side with die bonding material, and then welded to the epitaxial growth layer with solder wire to ensure power supply.
Solidifying materials mainly use silver paste that disperses silver particles into epoxy resin. This material has electrical conductivity and excellent thermal conductivity after hardening.
However, as it is made of resin material, deterioration problems may occur in short-wavelength leds and the like. Therefore, eutectic soldering such as AuSn is adopted in some leds. Eutectic soldering, like tin soldering and others, is entirely done with metal materials, featuring excellent thermal conductivity and high reliability. In addition, there is also a method similar to wire welding, which takes advantage of the softness and adhesiveness of gold to solder components with gold beads.
In recent years, LED components with insulating materials on the substrate have emerged. In this case, the power supply for both p and n semiconductors is carried out through the epitaxial growth layer. The bonding does not necessarily have to be conductive and transparent resin paste can be used.
Encapsulating Resin
The LED components are filled and fixed with resin around them. This can protect the LED components from moisture and external impacts. Use transparent resin or at least resin that can ensure the transmission of the luminous wavelength. The common longitudinal LED is one of the simplest forms in structure. The entire structure is supported by sealing resin, so high-hardness epoxy resin is often used. Hemispheres can be used as lenses to focus the light emitted by LED components.
Sealing resins are sometimes mixed with fillers such as diffusers to control photometric properties. In addition, with the advent of blue light-emitting components, phosphors began to be mixed into resins to convert blue light into any wavelength. In this way, white leds and leds of any chroma can be achieved.
The sealing resin directly covers the LED components and receives the light emitted by the components at close range. Therefore, the energy density of the light around the components is extremely high. When short-wavelength components such as blue and white leds are used, the light deterioration of the resin will become a major problem. The PLCC type packaging is supported by a forming frame (light box) and a lead frame structure, so silicone resin can be used. This resin is softer than epoxy resin but has high durability against light deterioration.
Formed frames (light boxes, reflective frames)
The PLCC type LED is equipped with a lead frame that conducts electricity to the resin-made frame. It is internally fitted with LED components and sealed with sealing resin to form an LED. It is supported by a formed frame structure, so soft sealing resin materials can be adopted. To effectively utilize the light of the LED components, the forming frame adopts a design to enhance the reflectivity and also adds white pigment as the resin filler.
The forming frame, like the sealing resin, has the function of protecting the interior of the LED from the influence of the external environment and needs to have excellent durability. When high reliability is required or it is used in harsh environments, ceramic frames with higher durability than resin can also be used.
Reflector / Lens
The refractive index of light in sealing resin is high. The shape of the sealing resin will cause the direction of light reaching the outside to change, thus having a lensing effect. The entire sealing resin of the longitudinal LED serves as a lens, controlling the light distribution characteristics of the LED. Surface mount leds can also be made into leds with acute directionality through the molding of sealing resin or by adding lenses later.
Diffusant
The photometric characteristics of LED components have specific patterns depending on different products. The photometric characteristics of leds sealed with transparent resin reflect the photometric characteristics of the LED components used. To make the light distribution mode uniform and eliminate the influence of component differences, diffusion materials such as silica can be mixed into the sealing resin.
[Phosphors]
After developing the blue light-emitting component, the fluorescent body can be excited by using the LED. In this way, leds of any color can be achieved through a single component. For instance, by combining a blue light-emitting element with a yellow phosphor and extracting the two kinds of light externally, white light can be obtained. (Figure 7)
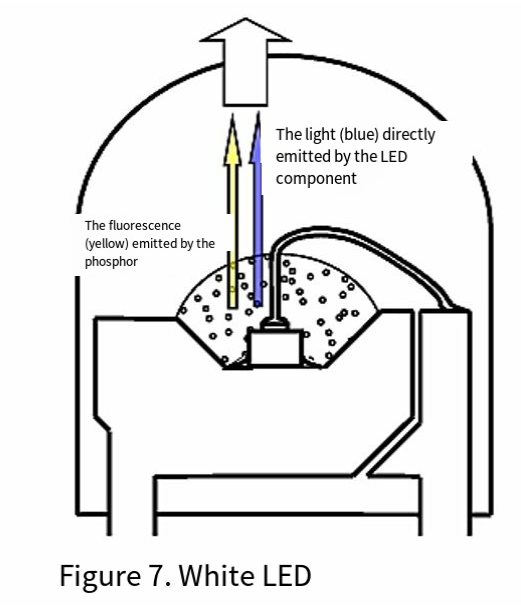
Phosphors are usually not moisture-resistant, and moisture-proof performance must be taken into account in LED design. In addition, some materials may cause deterioration of other components due to the components separated from them. Therefore, attention should be paid when choosing materials.
https://www.y-crystaled.net/basic-structure-of-leds.html
www.y-crystaled.net
Shenzhen Yuanjing Optoelectronics Technology Co., Ltd.
